CloudFormation Topology
The deployment has 4 redundant "shards" comprised of one Meet signalling server (which runs nginx, the Jitsi Meet frontend, prosody, and jicofo), and one or more autoscaled JVB servers, which run jitsi-videobridge2 for the actual audio/video traffic. Each shard is isolated from every other shard, but traffic will fail over automatically to a different shard via HAProxy if a full shard goes down. It optionally includes a coturn TURN server for NAT traversal, which is used by all shards.
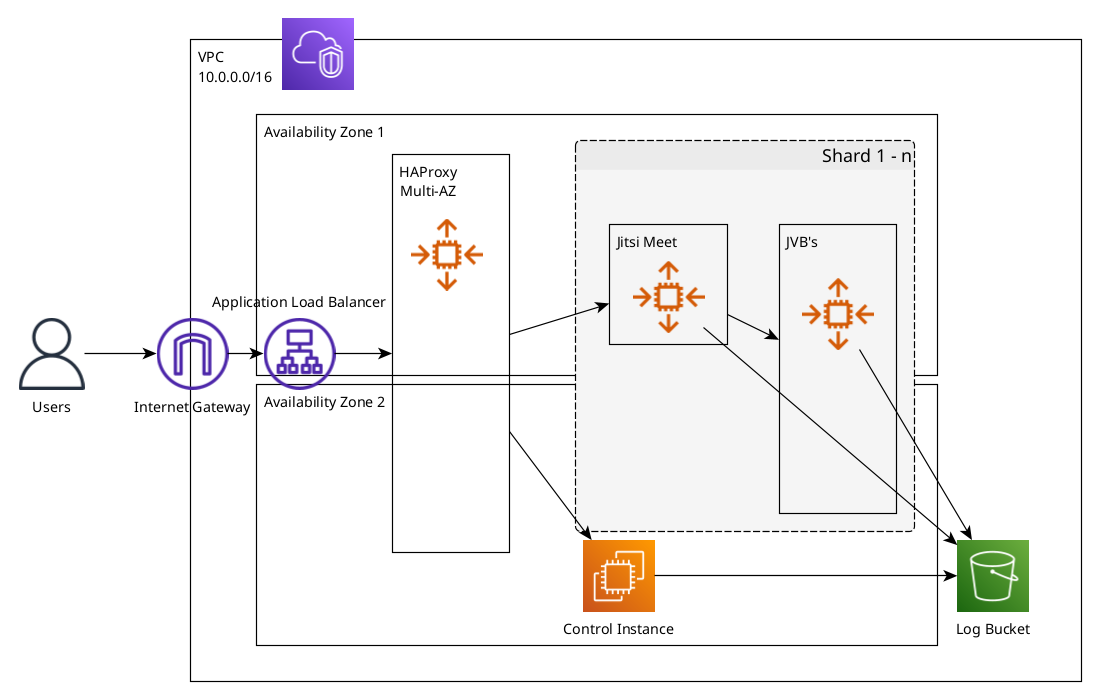
By default, only one shard is active at launch. As load increases on a single shard, it will autoscale the number of videobridges in that shard (at 70% average CPU), up to 50 bridges in a single shard (the Meet/signalling server can typically handle a large number of bridges before needing a second shard). You should be able to host thousands of participants in a single shard.
If you need additional redundancy or need to scale even further, you can manually enable additional shards. You can do this either via the AWS EC2 console by changing the desired number of instances in the appropriate autoscaling groups for the Meet server and JVB servers from 0 to 1, or you can use the utility command line tool jitsictl via SSH on the control server.
There are 5 types of EC2 instances created by the stack:
Control - this functions as the bastion host for SSH, runs the logging/monitoring infrastructure, and has management command line tools such as
jitsictl. There's only one Control instance per stack, which generally has low load.HAProxy - this handles load balancing traffic between shards. It will autoscale to more instances automatically if needed, but a single HAProxy can handle tens of thousands of requests a second.
Meet - this is the signalling/web server that runs the frontend, Prosody, and Jicofo, and handles load balancing between bridges in a single shard. There will only ever be one instance per active shard.
JVB - this handles the actual A/V traffic and runs jitsi-videobridge2. You will have between 1-50 bridges per shard, and they will scale up and down automatically based on traffic.
TURN (optional) - when enabled, this runs a coturn TURN/STUN server for NAT traversal for clients on restrictive networks. The stack uses a single TURN server, which can be scaled vertically to support your required number of users needing NAT traversal, and can support many thousands of users on a single instance.